
The blood circulatory system of mother and baby are distinct from one another.

If the baby is Rh-negative, that causes no problems.

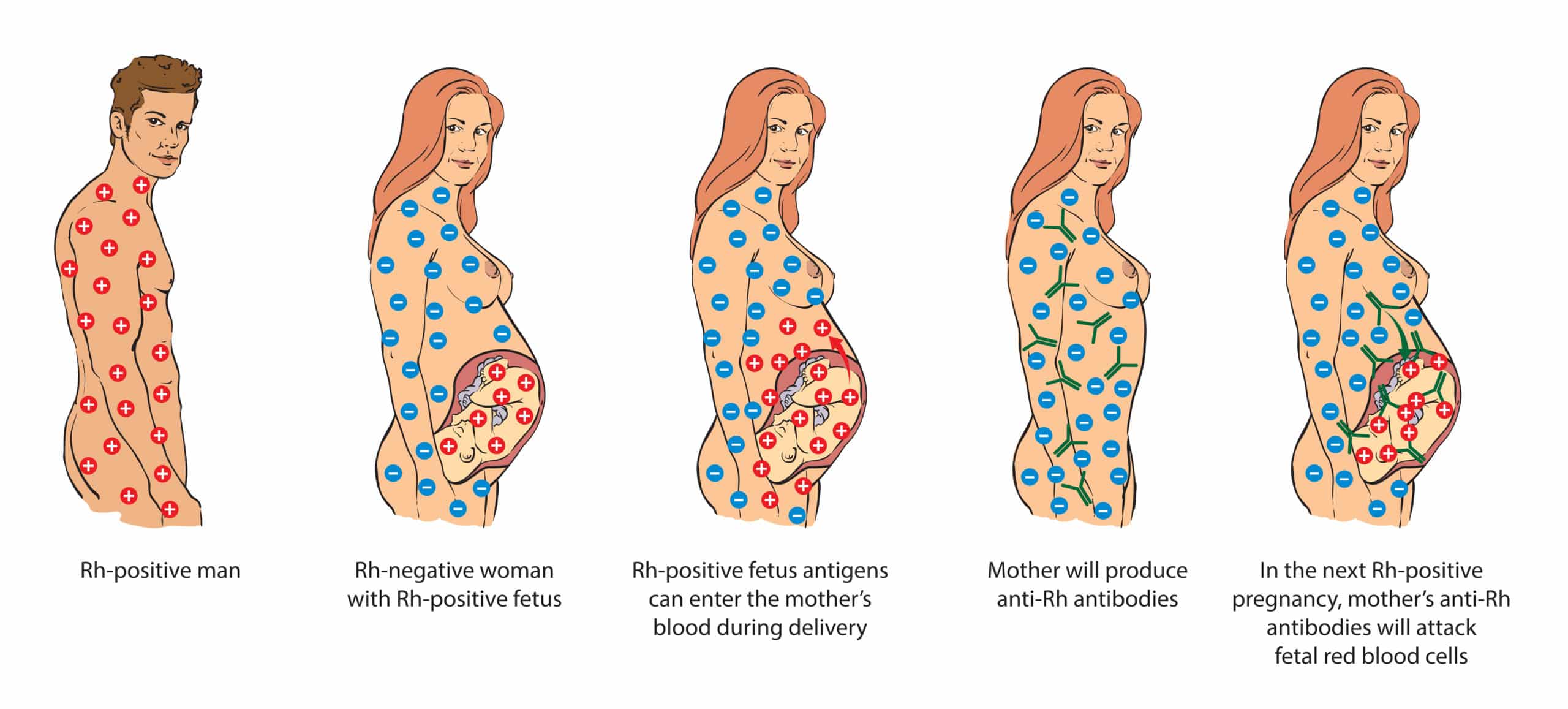
When an Rh-negative person conceives a baby with an Rh-positive person, the baby could be Rh-positive or Rh-negative. Because the Rh factor is inherited from either of the parents, the risk can increase greatly if the father of the baby is an Rh-positive individual. Statistically, 85 percent of individuals in the world are Rh-positive.
RH IFACTOR IN COMPABILITY MANUAL
The external manual rotation of a baby in a breech position - such as buttocks first - before labor.Injury or other trauma to your abdomen during pregnancy.Cordocentesis - a prenatal test in which a sample of the baby's blood is removed from the umbilical cord for testing.Chorionic villus sampling - a prenatal test in which a sample of the wispy projections that make up most of the placenta (chorionic villi) is removed for testing.Amniocentesis - a prenatal test in which a sample of the fluid that surrounds and protects a baby in the uterus (amniotic fluid) is removed for testing or treatment.Removal of a molar pregnancy - a noncancerous (benign) tumor that develops in the uterus.Ectopic pregnancy - when a fertilized eggs implants somewhere outside the uterus, usually in a fallopian tube.If you're Rh negative and your baby might be or is Rh positive, your health care provider may recommend an Rh immune globulin injection after situations in which your blood could come into contact with the baby's blood, including: If your baby is born Rh positive, you'll need another injection shortly after delivery. If your baby is born Rh negative, you don't need any other treatment. This prevents your body from producing Rh antibodies during your pregnancy. If you haven't started to produce Rh antibodies, you'll likely need a shot (injection) of a blood product called Rh immune globulin. That test is used to detect antibodies to Rh positive blood.

If you're Rh negative, you might need to have another blood test - called an antibody screen - several times: during your first trimester, during week 28 of pregnancy and when your baby is born. Red blood cells are needed to carry oxygen throughout the body. This could lead to life-threatening anemia, a condition in which red blood cells are destroyed faster than the baby's body can replace them. If your next baby is Rh positive, the Rh antibodies can cross the placenta and damage the baby's red blood cells. But problems can happen if you become pregnant again. Those antibodies aren't a problem during the first pregnancy. If you're Rh negative and your baby is Rh positive, your body might produce proteins called Rh antibodies if your blood and the baby's blood mix. It can also happen if you have bleeding or trauma to your abdomen during pregnancy. However, a small amount of your baby's blood could come in contact with your blood when the baby is born. Usually, your blood doesn't mix with your baby's blood during pregnancy. During pregnancy, problems can happen if you're Rh negative and your baby is Rh positive.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
